|
Mathematical model > Vascular model > Venous pulmonary model
|
Venous pulmonary model
The system of correlations (7) - (11) is concretized conformably to pulmonary veins (VR compartment).
Venous pulmonary pressure PVR is a pressure in the opening of right atrium, that is a part of venous pulmonary compartment (VR). This pressure is determined as a sum of a vascular component (7), and a component PVR0 , defined by atrium activity:
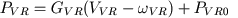 |
(38) |
In the formula (38) volumetric elasticity GVR describes rigidity properties of venous walls, ωVR - stressless volume in this section of vascular system. Values of volumetric elasticity and stressless volume decribe venous tone. In our model this value GVR linearly depends on neurohumoral factor γ, and the value ωVR is a parameter
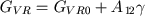 |
(39) |
For blood volume VVR differential equation of volumetric balance is given (formula variant (9)):
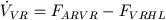 |
(40) |
Blood flow from left atrium to left ventricle through mitral valve is determined by this formula variant (21):
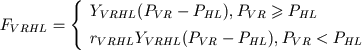 |
(41) |
The conductivity of this section of vascular model is evaluated with the equation:
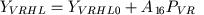 |
(42) |
The member A16PVR in the equation (42) evaluates the dependence of venous conductivity from venous pressure: pressure increase leads to an expansion of venous lumen and conductivity increase. In the equation (42) there is no member similar to "muscle" member A7RO2 in the equation for venous systemic conductivity (37).
Mathematical model > Vascular model > Venous pulmonary model
References on the topic:
© Samara-Dialog Ltd. 2004-2009 |